The alert management training file supports two categories of input columns:
- Predefined attributes (system-defined alert and resource fields)
- Custom attributes (user-defined tags for resources or alerts)
These columns define the matching logic used by the machine learning model to process incoming alerts.
Note
The training file for Alert Escalation and First Response policies now supports custom attributes from both resources and alerts as input fields. This enhancement allows you to implement more flexible and business-aligned alert handling rules.Predefined Attributes
Predefined attributes are system-provided fields derived from alert and resource data. These attributes typically follow a hierarchical structure with up to three levels.
Attribute Hierarchy Example
For the column name resource.generalInfo.resourceType:
resource= first level (alert object)generalInfo= second levelresourceType= third level
Only non-collection type attributes are supported, with a few noted exceptions.
Retrieving Predefined Attributes
To discover supported fields:
- Use the Get Alert API for alert attributes.
- Use the Get Resource API for resource attributes.
Example Attributes
| Alert Attributes | Alert Resource Attributes |
|---|---|
clientUniqueId | resource.state |
metric | resource.generalInfo.resourceType |
component | resource.generalInfo.make |
alertType | resource.generalInfo.osName |
currentState | resource.location.name |
status | resource.deviceGroup.name |
priority | resource.serviceGroup.name |
elapsedTimeString | resource.dnsName |
healedTimeString | Not applicable |
repeatCount | Not applicable |
Note
resource.deviceGroup.name and resource.serviceGroup.name are collection-type attributes but are supported due to their importance in routing and prioritization.Unsupported Attributes
resource.generalInfo.nameis not supported in training files.- Resource names are dynamic and require constant maintenance.
- Instead, use stable attributes such as:
resource.generalInfo.resourceTyperesource.deviceGroup.nameresource.serviceGroup.name
Custom Attributes
Custom attributes (also known as tags) are user-defined fields that can be applied to resources or alerts. These attributes are useful for routing, escalation, or suppression based on business logic, such as tiers, environments, or application roles.
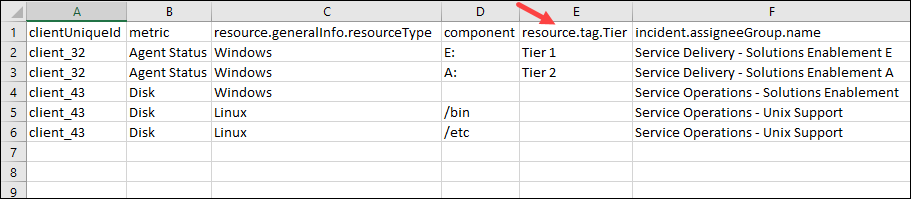
Example: Tier-Based Routing Using Resource Tags
| resource.tag.Tier | incident.assigneeGroup.name |
|---|---|
| Tier 1 | Critical Support |
| Tier 2 | Infrastructure Support |
| Tier 3 | General Support |
Using Alert-Level Tags
You can also use custom attributes applied to alerts directly. These should be formatted as tag.<tag_name>.
Example for Alert Escalation
| tag.environment | incident.assigneeGroup.name |
|---|---|
| Production | Prod Support |
| QA | QA Support |

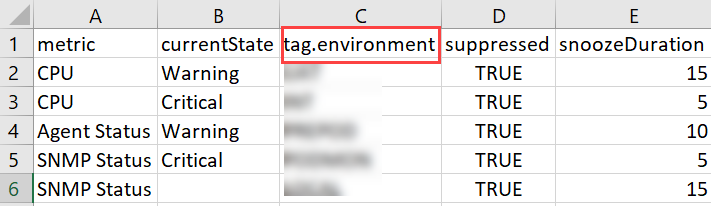
Example for First Response
| tag.environment | suppressed | snoozeDuration |
|---|---|---|
| QA | true | 30 |
Multi-Level Group Path Formatting
When using group-based attributes such as resource.deviceGroup.name or resource.serviceGroup.name:
- To specify nested groups, provide the full group path:
- Example:
Parent > Child > GrandChild
- Example:
- For direct child groups:
- Example:
Parent > Child
- Example:
This ensures that the rule correctly maps to the group hierarchy used in your OpsRamp environment.